| Dong Ah Shin | 3 Articles |
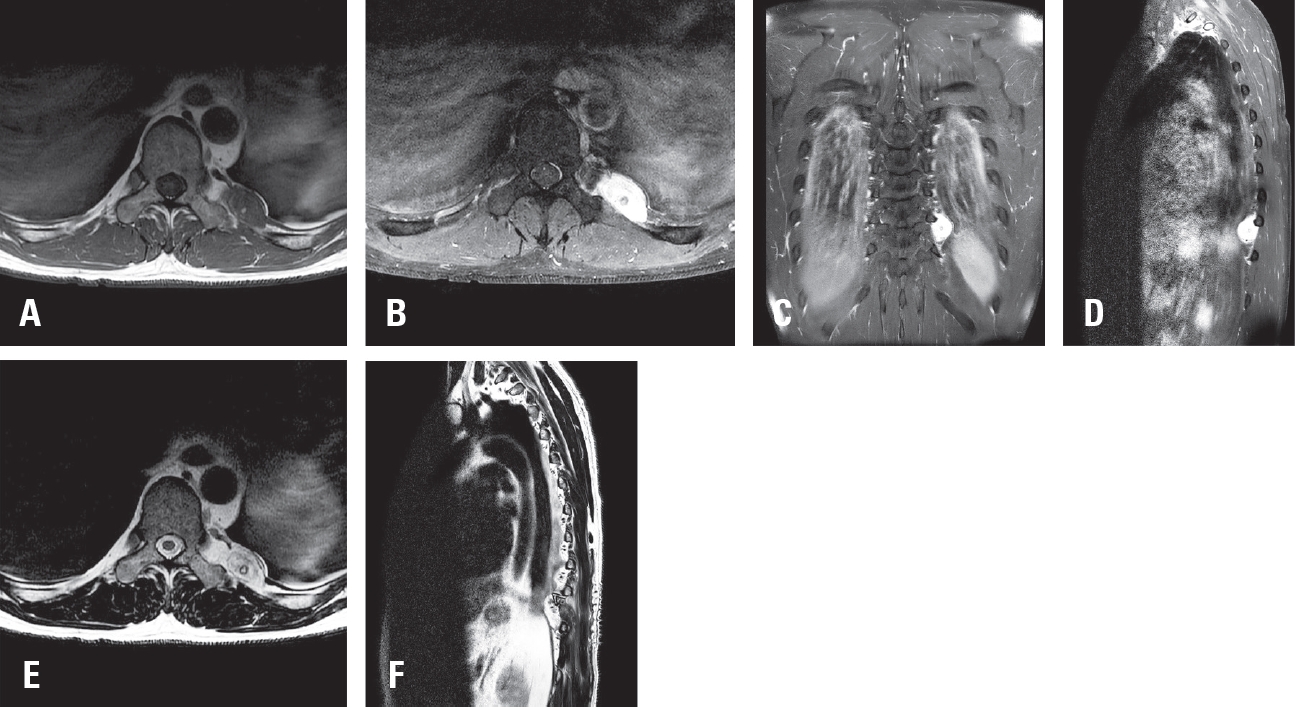
Purpose
Glomangiomas of the spine are exceptionally rare benign vascular tumors, frequently misdiagnosed as more common lesions such as schwannomas or meningiomas. Although most spinal glomangiomas exhibit benign behavior, the presence of a BRAF V600E mutations may indicate uncertain malignant potential. Accurate diagnosis and complete surgical excision are essential for favorable outcomes. Methods A 43-year-old male with left flank pain was evaluated with thoracic MRI and underwent surgical resection. Histopathological and molecular analyses were performed. Results Thoracic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed a 2.8 cm ovoid, hypervascular mass adjacent to left T10 transverse process, extending to the posterior hemithorax. Surgical resection was performed, and histopathological examination confirmed a glomangioma with positive smooth muscle actin (SMA) expression and a BRAF V600E mutation. Conclusions This case highlights the diagnostic challenge posed by paraspinal glomangiomas and emphasizes the importance of histopathological and molecular analysis in establishing the correct diagnosis. A review of the literature demonstrates that complete surgical excision remains the treatment of choice, with excellent prognosis. The identification of BRAF mutations may warrant closer follow up.
Objective
To evaluate the efficacy and safety of anorganic bone matrix (ABM)/P-15 compared with local autograft bone in posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) with pedicle screws for degenerative lumbar diseases. Methods This is a retrospective analysis of consecutive series of 138 patients undergoing 1 or 2 levels PLIF from 2015 to 2020 in our single institute. Local autograft bone or ABM/P-15 (i-factor, Cerapedics Inc., Westminster, Colorado USA) were used for interbody fusion. The successful fusion was defined as the segmental cobb angle of less than 5 degrees of in flexion/extension X-rays and continuity of the trabecular bony bridging in computed tomography (CT) images. Results Among a total of 138 patients, total levels of fusion were 202, of which 74 were in 1 level fusion and 128 were in 2 level fusion. And 93 used ABM/P-15 and 109 used local autograft bone. The evaluation time of fusion status was 1 year after surgery. Successful fusion based on X-ray images was achieved 84.1% (90/107) for local autograft bone and 91.3% (84/92) for ABM/P-15 (p=0.127). Based on CT images, 86.9% (93/107) of autograft group and 95.6%(87/91) of AMP/P-15 group showed successful fusion respectively (p=0.034). Occurrence rate of autolysis was 14% (15/107) for local autograft bone and 17.6% (16/91) for ABM/P-15. Subsidence rates were 11.2% (12/107) for local autograft bone and 9.99% (9/91) for ABM/P-15. Hollow formation around pedicle screw was noted in 9.3% (10/107) for local autograft bone and 2.2% (2/91) for ABM/P-15. Conclusions The use of AMP/P-15 for lumbar interbody fusion surgery can be a good substitute for local autograft bone in terms of better fusion rate and similar complication rate on radiologically.
Objective
This study aimed to compare the efficacy of unilateral biportal endoscopic decompression (UBE) and percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy (PELD) in reducing muscle injury by measuring serum levels of creatine phosphokinase (CK) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). Materials and Methods Thirty patients with degenerative lumbar stenosis or a herniated lumbar disc underwent decompression surgery. Among them, 12 patients underwent UBE (experimental group, n=12) and 18 underwent PELD (control group, n=18). CK and LDH were determined at admission and 1, 3, and 5 days after surgery. Pain was measured with a visual analogue scale (VAS). Results The mean age was significantly higher in the UBE group than the PELD group (63.33±13.50 vs. 49.94±14.79, p<0.035). Mean CK levels were not significantly different at admission. However, at both 3 and 5 days after surgery, CK levels were higher in the UBE group (308.44±153.93 vs. 70.43±40.15, p=0.002; 157.11±91.41 vs. 47.62±23.13, p=0.007). The mean LDH level was higher in the PELD group at 1 day after surgery (152.55±34.69 vs. 199.87±53.78, p=0.027). The operation time was significantly shorter in the PELD group (90.67±39.59 vs. 49.43±14.11, p=0.003). Conclusions The UBE group had higher CK levels at 3 and 5 days after surgery. The PELD group had a higher LDH level at 1 day after surgery. Therefore, neither procedure is clearly superior in terms of muscle damage.
|
|

